This week’s cyber intel brief covers Microsoft vulnerabilities, MS-ISAC funding cuts, and AI-driven APT activity threatening critical infrastructure.
TLP: CLEAR
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The week of September 6-12, 2025 featured significant operational disruptions to U.S. critical infrastructure protection capabilities and continued nation-state cyber operations. Microsoft's Patch Tuesday delivered 80+ vulnerability fixes including critical SMB and NTLM flaws, while the termination of MS-ISAC federal funding effective September 30 creates immediate operational gaps for over 18,000 state, local, tribal, and territorial government organizations.
Concurrently, coordinated Chinese and North Korean Advanced Persistent Threat groups demonstrated evolution in attack methodologies, with Chinese APTs maintaining persistent access to global telecommunications infrastructure since 2021 and North Korean groups weaponizing artificial intelligence and legitimate cloud services for covert operations.,,
CRITICAL INCIDENTS
1. Microsoft September 2025 Patch Tuesday Addresses 80+ Critical Vulnerabilities
Microsoft released patches for 80-86 vulnerabilities on September 10, 2025, including eight Critical and 72 Important severity flaws with no actively exploited zero-days but two publicly disclosed vulnerabilities., Critical priorities include CVE-2025-54918 (Windows NTLM elevation of privilege, CVSS 8.8), CVE-2025-54910 (Microsoft Office RCE via Preview Pane, CVSS 8.4), and CVE-2025-55232 (Microsoft HPC Pack RCE with potential wormable characteristics)., The release represents the third NTLM vulnerability in 2025, indicating systemic authentication weaknesses requiring enterprise-wide remediation. SMB relay vulnerability CVE-2025-55234 (CVSS 8.8) was publicly known prior to patching, elevating exploitation risk across enterprise networks.
Analyst Comment: The concentration of critical SMB and NTLM vulnerabilities combined with Office Preview Pane attack vectors creates significant enterprise risk.
2. MS-ISAC Federal Funding Termination Creates Critical Infrastructure Protection Gap
Federal funding for Multi-State Information Sharing & Analysis Center operations officially terminated September 30, 2025, affecting cybersecurity services for over 18,000 U.S. state, local, tribal, and territorial government organizations. Ten categories of services were discontinued including cyber threat analysis, threat distribution, incident response services, and member support, with organizations failing to transition to fee-based membership experiencing service disruptions starting October 1., Critical federally-funded services including Albert Network Monitoring, Malicious Domain Blocking and Reporting, and cybersecurity advisories remained operational through September 30 but face uncertain continuity.
Analyst Comment: This operational disruption creates immediate vulnerability in critical infrastructure protection at the precise moment nation-state threat activity is escalating.
3. Canadian Government Multi-Factor Authentication Service Compromised
The Canadian government disclosed a cyber incident affecting the multi-factor authentication service used by Canada Revenue Agency, Employment and Social Development Canada, and Canada Border Services Agency on September 9, 2025. The incident occurred August 3-15, 2025, via a vulnerability in 2Keys Corporation's MFA service during routine software updates, resulting in malicious actor access to phone numbers and email addresses and subsequent spam phishing campaigns. Government services continuity was maintained throughout the incident, with the vulnerability patched and services restored. The incident highlights supply chain risks in third-party authentication services critical to government operations.
Analyst Comment: This incident demonstrates the cascading security risks inherent in outsourced authentication services and the need for enhanced supplier security requirements across critical government functions.
ACTIVE THREAT ACTORS
North Korean APT Coordination Campaign (Lazarus, APT37, Kimsuky)
North Korean Advanced Persistent Threat groups demonstrated coordination and technical evolution during the collection period, with Lazarus APT weaponizing ClickFix social engineering techniques in fake recruitment campaigns targeting government and defense contractors. APT37 deployed new Rust-based Rustonotto backdoor and enhanced FadeStealer capabilities using Transactional NTFS evasion and comprehensive surveillance tools including keylogging and audio recording. Kimsuky operations leveraged weaponized GitHub repositories for command-and-control communications, using hardcoded private tokens and scheduled task persistence with GUID naming patterns. The coordinated campaign targeted South Korean government entities, Taiwan academia, and U.S. defense contractors with sophisticated supply chain attacks and AI-powered exploitation frameworks.
Chinese Network Infrastructure Compromise Coalition (Salt Typhoon, UNC4841, Multiple APTs)
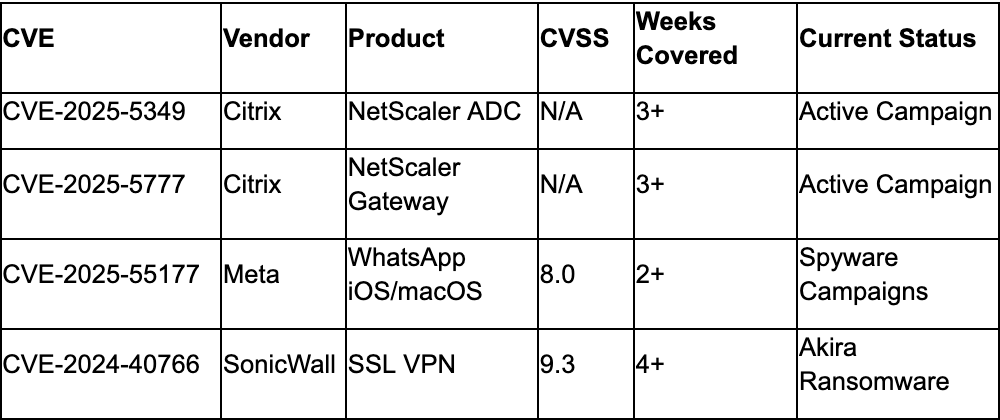
Intelligence confirms sustained Chinese state-sponsored compromise of global network edge devices since 2021, with Salt Typhoon and UNC4841 conducting joint operations exploiting known CVEs in backbone, provider edge, and customer edge routers.,The campaign establishes persistence through modified Access Control Lists and deploys GRE/IPsec tunnels for covert lateral movement across telecommunications, government, transportation, and military infrastructure. Additional Chinese APT41 operations targeted U.S.-China trade negotiations through spear-phishing campaigns impersonating congressional representatives before critical Sweden talks. The systematic approach demonstrates coordinated strategic intelligence collection supporting broader geopolitical objectives.
Storm-0501 Hybrid Cloud Evolution
Microsoft-tracked Storm-0501 evolved from traditional ransomware operations to sophisticated hybrid cloud exploitation without malware deployment, targeting healthcare, financial services, IT, and education sectors. The group exploits misconfigured Entra ID identities and Connect Sync accounts, using Azure-native tools for data exfiltration and backup destruction while exploiting visibility gaps between on-premises and cloud security. This evolution represents a significant shift in ransomware tactics toward cloud-native attacks that bypass traditional endpoint detection and response solutions, requiring fundamental changes in hybrid cloud security architecture.
TRENDS
AI-Powered Threat Capability Emergence
Analysis reveals the first confirmed AI-powered ransomware "PromptLock" using local generative language models to dynamically create malicious Lua scripts, written in Golang with cross-platform compatibility. This development coincides with the emergence of "Hexstrike-AI" exploitation framework reducing exploit development time from days to minutes, and critical vulnerabilities in AI-powered development tools including Cursor IDE CVE-2025-54136 enabling silent code execution., The convergence indicates AI technologies are simultaneously creating new attack vectors while lowering barriers to sophisticated cyber operations.
Analyst Comment: The weaponization of artificial intelligence for automated attack generation represents a fundamental shift requiring enhanced behavioral detection and AI-specific security controls.
Critical Vulnerability Exploitation Pattern Acceleration
Data analysis across the collection period reveals accelerated exploitation of critical infrastructure vulnerabilities, with CISA adding DELMIA Apriso CVE-2025-5086 to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog and confirmed active exploitation of SAP NetWeaver CVE-2025-42944 (CVSS 10.0)., Industrial control systems faced nine separate CISA advisories on September 9, while Australian ACSC confirmed active exploitation of NetScaler vulnerabilities CVE-2025-5349 and CVE-2025-5777 affecting critical infrastructure globally., The pattern indicates threat actors are systematically targeting industrial and enterprise systems with shortened vulnerability-to-exploitation timelines.
Analyst Comment: The compression of vulnerability disclosure to active exploitation cycles requires fundamental changes in patch management and threat monitoring for critical infrastructure operators.
Legitimate Service Abuse Escalation
Intelligence indicates significant escalation in threat actor abuse of legitimate cloud and development services, with cybercriminals exploiting compromised AWS credentials for 50,000+ daily phishing emails via Simple Email Service and sophisticated campaigns abusing Google AppSheet infrastructure to bypass email authentication., GitHub platforms were weaponized by Kimsuky APT for command-and-control operations, while malicious Chrome extensions targeted Meta advertising credentials through deceptive domain registration., The trend demonstrates threat actors systematically exploiting trusted platform legitimacy to evade traditional security controls.
Analyst Comment: The systematic abuse of legitimate cloud and development platforms require enhanced behavioral monitoring and stricter application security controls across enterprise environments.
VULNERABILITIES
Critical Patches Required This Month
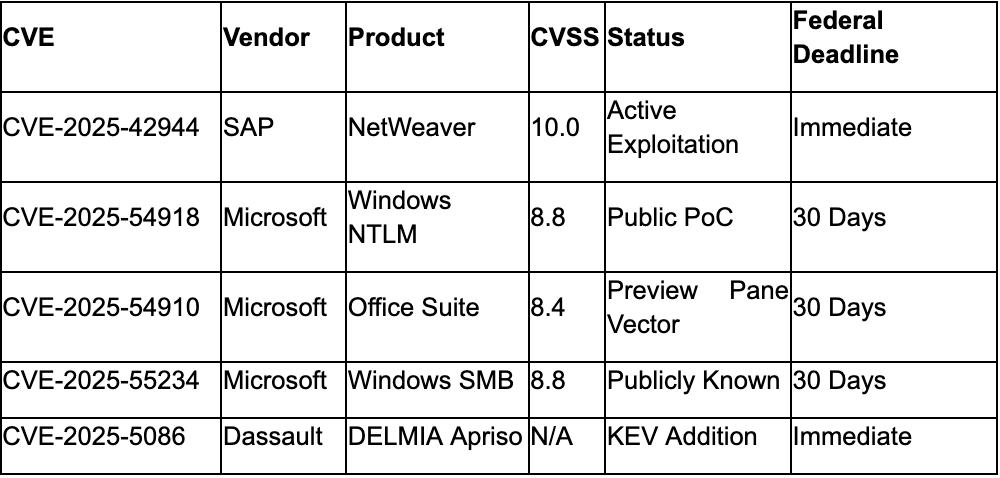
Continuing Active Exploitation
RECOMMENDATIONS
Immediate Actions (0-24 Hours)
- Apply SAP NetWeaver patches for CVE-2025-42944 immediately given CVSS 10.0 rating and confirmed active exploitation
- Deploy Microsoft September Patch Tuesday updates prioritizing SMB and NTLM vulnerabilities on critical systems
- Implement emergency monitoring for MS-ISAC service gaps affecting SLTT organizations before October 1 deadline
- Enable Enhanced Protection for Authentication and SMB signing on all Windows systems
- Block identified command-and-control infrastructure associated with North Korean and Chinese APT campaigns
- Abrams, L. (2025, September 9). Microsoft September 2025 Patch Tuesday fixes 81 flaws, two zero-days. BleepingComputer.
- Microsoft and Adobe Patch Tuesday, September 2025 Security Update Review. (2025, September 9). Qualys. https://blog.qualys.com/vulnerabilities-threat-research/2025/09/09/microsoft-patch-tuesday-september-2025-security-update-review
- Center for Internet Security. (2025, September). MS-ISAC at a glance. https://www.cisecurity.org/ms-isac
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). Lazarus APT hackers using ClickFix technique to steal sensitive intelligence data. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/lazarus-apt-hackers-using-clickfix-technique/
- Tata Communications. (2025, September 9). Weekly threat intelligence advisory report. Tata Communications Cyber Security Response Centre.
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). Chinese Salt Typhoon and UNC4841 hackers teamed up to attack government and corporate infrastructure. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/chinese-salt-typhoon-and-unc4841-hackers-teamed-up/
- CrowdStrike. (2025, September 9). September 2025 Patch Tuesday: Updates and Analysis. CrowdStrike Blog. https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/blog/patch-tuesday-analysis-september-2025/
- Check Point Research. (2025, September 8). 8th September -- Threat Intelligence Report. Check Point Research. https://research.checkpoint.com/2025/8th-september-threat-intelligence-report/
- The Hacker News. (2025, September 10). Microsoft fixes 80 flaws --- Including SMB PrivEsc and Azure CVSS 10.0 bugs. The Hacker News. https://thehackernews.com/2025/09/microsoft-fixes-80-flaws-including-smb.html
- Tenable. (2025, September 9). September 2025 Microsoft Patch Tuesday. Tenable Blog. https://www.tenable.com/blog/microsofts-september-2025-patch-tuesday-addresses-80-cves-cve-2025-55234
- Ullrich, J. (2025, September 9). Microsoft Patch Tuesday September 2025. SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu/diary/32270
- Center for Internet Security. (2025). MS-ISAC membership FAQ. https://www.cisecurity.org/ms-isac/ms-isac-membership-faq
- Center for Internet Security. (2025, September 10). MS-ISAC cyber threat alert level. MS-ISAC Cybersecurity Threats. https://www.cisecurity.org/cybersecurity-threats
- Center for Internet Security. (2025, September 9). Multiple vulnerabilities in Adobe products could allow for arbitrary code execution. MS-ISAC Toolkit. https://www.cisecurity.org/ms-isac/ms-isac-toolkit
- Center for Internet Security. (2025, September 9). Multiple vulnerabilities in Ivanti products could allow for remote code execution. MS-ISAC Toolkit. https://www.cisecurity.org/ms-isac/ms-isac-toolkit
- Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat. (2025, September 9). Statement from the Office of the Chief Information Officer of the Government of Canada on a Data Security Incident. Government of Canada. https://www.canada.ca/en/treasury-board-secretariat/news/2025/09/statement-from-the-office-of-the-chief-information-officer-of-the-government-of-canada-on-data-security-incident.html
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). Lazarus APT hackers using ClickFix technique to steal sensitive intelligence data. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/lazarus-apt-hackers-using-clickfix-technique/
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). New APT37 attacking Windows machines with new Rust and Python based malware. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/new-apt37-attacking-windows-machines/
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). Kimsuky hackers via weaponized LNK file abuses GitHub for malware delivery. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/kimsuky-hackers-via-weaponized-lnk-file/
- Tata Communications. (2025, September 9). Weekly threat intelligence advisory report. Tata Communications Cyber Security Response Centre.
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). Exposed 'Kim' dump exposes Kimsuky hackers new tactics, techniques, and infrastructure. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/exposed-kim-dump-exposes-kimsuky-hackers/
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). U.S. authorities investigating malicious email targeting trade talks with China. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/u-s-authorities-investigating-malicious-email/
- Tata Communications. (2025, September 9). Weekly threat intelligence advisory report. Tata Communications Cyber Security Response Centre.
- Tata Communications. (2025, September 9). Weekly threat intelligence advisory report. Tata Communications Cyber Security Response Centre.
- Check Point Research. (2025, September 8). 8th September -- Threat Intelligence Report. Check Point Research. https://research.checkpoint.com/2025/8th-september-threat-intelligence-report/
- The Hacker News. (2025, September). Cursor AI code editor flaw enables silent code execution via malicious repositories. The Hacker News. https://thehackernews.com/2025/09/cursor-ai-code-editor-flaw-enables.html
- CISA. (2025, September 11). CISA adds one known exploited vulnerability to catalog. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency. https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/alerts/2025/09/11/cisa-adds-one-known-exploited-vulnerability-catalog
- The Hacker News. (2025, September 10). SAP patches critical NetWeaver (CVSS up to 10.0) and high-severity S/4HANA flaws. The Hacker News. https://thehackernews.com/2025/09/sap-patches-critical-netweaver-cvss-up.html
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency. (2025, September 9). Industrial Control Systems Advisories ICSA-25-252-01 through ICSA-25-252-09. U.S. Department of Homeland Security. https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories
- Australian Cyber Security Centre. (2025, September). Critical vulnerabilities in Citrix NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway products. Alerts and advisories. https://www.cyber.gov.au/about-us/view-all-content/alerts-and-advisories
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). Hackers weaponize Amazon Simple Email Service to send 50,000+ malicious emails per day. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/hackers-weaponizee-amazon-simple-email-service/
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). New phishing attack mimics Google AppSheet to steal login credentials. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/new-phishing-attack-mimics-google-appsheet/
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). Malicious Chrome extension attacking users to steal Meta login credentials. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/malicious-chrome-extension-attacking-users/
- Cybersecurity News. (2025, September). New GONEPOSTAL malware hijacking Outlook to enable command and control communication. Cybersecurity News. https://cybersecuritynews.com/new-gonepostal-malware-hijacking-outlook/


