Stay up to date the most pressing cyber threats, emerging trends and what they mean for enterprise security, critical infrastructure and global risk.
TLP: CLEAR
Executive Summary
Intelligence collection for July 12-18, 2025 reveals multiple high-impact cyber incidents requiring immediate attention. Chinese APT Salt Typhoon maintained 9-month access to US National Guard networks across all 50 states, compromising administrator credentials and network diagrams. Active zero-day exploitation continues with Google Chrome's CVE-2025- 6558 marking the fifth Chrome zero-day exploited in 2025, while NVIDIA's container escape vulnerability affects 37% of AI cloud environments.
Nation-state and cybercriminal threat actors demonstrate continued targeting of US interests through multiple vectors. Iranian-backed Pay2Key ransomware operations offer increased profit sharing for attacks on US and Israeli targets, while law enforcement successfully disrupted the NoName057(16) hacktivist network across 12 countries.
Analyst Comment: The Salt Typhoon compromise affects US state-level cyber defense coordination, while multiple critical vulnerabilities require immediate federal patching to prevent further exploitation.
Critical Incidents
1. Salt Typhoon Compromises US National Guard Networks
Chinese APT Salt Typhoon maintained persistent access to US state Army National Guard networks for nine months (March-December 2024), with data exfiltration capabilities extending to network counterparts across all 50 US states and 4 territories.1Intelligence indicates the compromise enabled access to administrator credentials, network diagrams, geographic locations, and personally identifiable information of service members, with broader campaign stealing 1,462 network configuration files from approximately 70 US government and critical infrastructure entities across 12 sectors.2 The compromise threatens state-level cybersecurity partners' ability to defend US critical infrastructure, particularly concerning since 14 states have National Guard units integrated with fusion centers for threat intelligence sharing.
Analyst Comment: This compromise affects US state-level defense infrastructure coordination, providing China access to American cyber defense mechanisms.
2. Google Chrome Zero-Day CVE-2025-6558 Active Exploitation
Google's Threat Analysis Group confirmed active exploitation of CVE-2025-6558, a Chrome ANGLE GPU validation vulnerability (CVSS 8.8) allowing sandbox escape through crafted HTML pages.3 This marks the fifth Chrome zero-day of 2025 under active exploitation, with evidence suggesting nation-state or surveillance-focused targeting given TAG involvement.4 The vulnerability affects Chrome's Almost Native Graphics Layer Engine, providing attackers a rare but powerful path to deeper system access across enterprise and consumer environments.
Analyst Comment: The continued discovery of Chrome zero-days indicates sustained research efforts targeting the browser platform.
3. North Korean npm Supply Chain Attack Escalation
North Korean threat actors published 67 malicious npm packages with over 17,000 downloads, deploying new XORIndex malware loader alongside existing HexEval campaigns as part of the Contagious Interview operation targeting developers.5 The packages serve as conduits for BeaverTail stealer and InvisibleFerret backdoor deployment, representing a "whack-a-mole" dynamic with rapid adaptation to detection efforts. This campaign demonstrates sophisticated understanding of developer workflows and creates multiplicative effects as compromised developers can introduce vulnerabilities into multiple downstream software products.
Analyst Comment: Supply chain attacks targeting development environments create cascading risks across the software ecosystem requiring enhanced developer security controls.
4. Matanbuchus 3.0 Microsoft Teams Campaign
Threat actors are distributing Matanbuchus 3.0 malware through sophisticated social engineering campaigns impersonating Microsoft Teams IT helpdesk calls, with premium pricing of $10,000/month (HTTP) and $15,000/month (DNS)—representing a 4x increase from original versions.6 The malware-as-a-service features advanced in-memory capabilities, enhanced obfuscation, and CMD/PowerShell reverse shells, using Quick Assist for remote access and PowerShell script deployment.7 Campaigns target real estate and finance companies in the US and Europe, serving as a precursor to ransomware deployment including Black Basta operations.
Analyst Comment: The Teams impersonation represents evolution in social engineering tactics exploiting trusted collaboration platforms during remote work environments.
5. Google Gemini AI Prompt Injection Vulnerability
Security researchers disclosed "Phishing for Gemini" attacks using invisible HTML and CSS to inject malicious prompts into Gemini for Workspace email summarization features.8 The vulnerability requires no links or attachments, using hidden text techniques (font-size:0, white-on-white) to generate fake security alerts appearing to originate from Google itself.9 The attack vector extends beyond email to affect Google Docs, Slides, and Drive, with potential for "AI worms" that could propagate across connected AI systems.
Analyst Comment: AI prompt injection represents a new attack surface requiring security controls as organizations integrate AI tools into business workflows.
Active Threat Actors
Iranian Pay2Key Ransomware Operations
Iranian-backed Pay2Key.I2P represents the first RaaS platform hosted entirely on I2P network infrastructure, offering unprecedented 80% profit share (increased from 70%) for attacks targeting "enemies of Iran"—primarily US and Israeli organizations.10 Intelligence indicates the operation has collected $4 million in ransoms across 51+ successful attacks in 4 months, with links to Fox Kitten APT group and incorporation of Mimic ransomware capabilities.11 The platform promotes across Russian and Chinese darknet forums with $20,000 per successful attack, emerging amid escalating US-Iran tensions following airstrikes on Iranian nuclear facilities.
CL-STA-1020 Southeast Asian Government Targeting
Advanced threat cluster CL-STA-1020 is conducting sophisticated espionage operations against Southeast Asian governments using novel HazyBeacon backdoor with AWS Lambda URLs as command and control infrastructure.12 The campaign focuses on collecting sensitive government data including information about trade disputes and tariffs, with exfiltration conducted through legitimate services including Google Drive and Dropbox to blend with normal traffic. This represents advanced tradecraft evolution enabling threat actors to hide malicious C2 communications within legitimate cloud service traffic.
Scattered Spider Following UK Arrests
UK National Crime Agency arrested four Scattered Spider members, including two 19-year olds, one 17-year-old, and one 20-year-old woman, on charges including Computer Misuse Act offenses, blackmail, and money laundering.13 The arrests targeted individuals responsible for attacks on major UK retailers including Marks & Spencer, Co-op, and Harrods, with connections to the wider cybercrime collective "The Com". Despite law enforcement action, Scattered Spider continues operations using sophisticated social engineering, phishing, SIM swapping, and extortion techniques against major airlines and enterprises.
Trends
Critical Infrastructure Hacktivist Campaign Escalation
Analysis reveals a 150% increase in hacktivist attacks targeting critical infrastructure during Q2 2025, with Z-Pentest group conducting 38 ICS attacks and newly emerged Dark Engine responsible for 26 ICS-targeted incidents.14 Italy represents the most frequently targeted country for industrial control system attacks, with Energy & Utilities sector identified as the primary target with coordinated timing suggesting deliberate collaboration between hacktivist groups. This escalation coincides with increased geopolitical tensions and demonstrates hacktivist groups' evolving capabilities against operational technology environments.
Analyst Comment: The coordinated timing suggests deliberate collaboration between hacktivist groups, indicating potential state direction or coordination of supposedly independent actor activities.
Law Enforcement Disruption Operations
Analysis reveals multiple successful law enforcement actions during the collection period, including the Armenian Ryuk ransomware operator Karen Serobovich Vardanyan's extradition to the US facing charges for $15 million in Bitcoin ransoms from 2,400+ attacks during 2019-2020.15 International Operation Eastwood successfully dismantled NoName057(16) hacktivist infrastructure across 12 countries, resulting in arrests in France and Spain and seizure of over 100 systems supporting the Russian-backed DDoS botnet.16 UK National Crime Agency arrests of four Scattered Spider members demonstrate continued pressure on major cybercrime operations targeting critical infrastructure and enterprise systems.
Analyst Comment: Coordinated international law enforcement demonstrates effective disruption capabilities against both nation-state proxies and cybercriminal enterprises.
Hyper-Volumetric DDoS Attack Evolution
Cloudflare recorded a 7.3 Tbps DDoS attack that peaked within 45 seconds, sustaining 4.8 billion packets per second and representing a 592% increase in attacks exceeding 100 million packets per second during Q2 2025.17 The attack targeted telecommunications and IT services sectors, with DemonBot variant identified infecting Linux IoT devices to build attack infrastructure. Analysis indicates Cloudflare blocked over 6,500 hyper-volumetric attacks in Q2 2025, demonstrating escalating DDoS capabilities that threaten critical service availability and network infrastructure resilience.
Analyst Comment: The scale of modern DDoS attacks requires updated infrastructure protection strategies as threat actors leverage expanding IoT attack surfaces.
Vulnerabilities
Critical Patches Required This Month
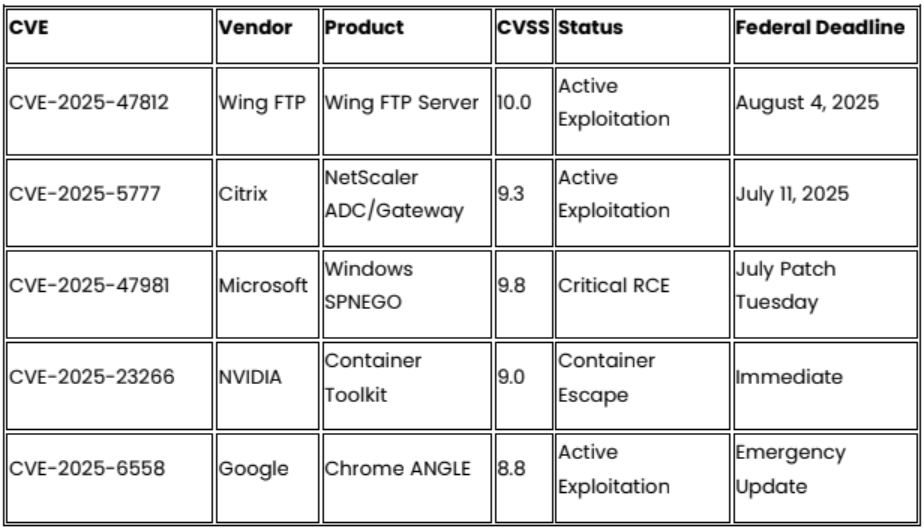
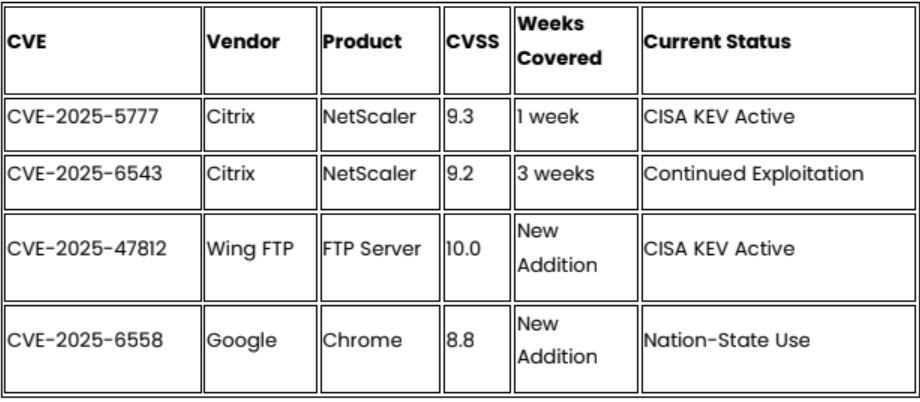
Continuing Active Exploitation
Recommendations
Immediate Actions (0-24 Hours)
- Prioritize patching of Citrix NetScaler and Wing FTP Server systems due to confirmed active exploitation and CISA KEV mandates
- Implement emergency Chrome browser updates across all enterprise environment to address CVE-2025-6558 zero-day exploitation
- Review npm package validation processes and implement enhanced developer workstation security controls following North Korean supply chain targeting
- Assess AI tool integration security controls in response to Gemini prompt injection vulnerabilities affecting business workflows
- Industrial Cyber. (2025, July 17). DHS: Salt Typhoon hackers breached Army National Guard, exposing admin credentials and network diagrams. https://industrialcyber.co/critical-infrastructure/dhs-salt-typhoon-hackers-breached-army-national-guard-exposing-admin-credentials-and-network-diagrams/
- NBC News. (2025, July 15). National Guard hacked by Chinese 'Salt Typhoon' campaign for nearly a year, DHS memo says. https://www.nbcnews.com/tech/security/national-guard-was-hacked-chinas-salt-typhoon-group-dhs-says-rcna218648
- Help Net Security. (2025, July 16). Update Google Chrome to fix actively exploited zero-day (CVE-2025-6558). https://www.helpnetsecurity.com/2025/07/16/update-google-chrome-to-fix-actively-exploited-zero-day-cve-2025-6558/
- The Hacker News. (2025, July 16). Urgent: Google releases critical Chrome update for CVE-2025-6558 exploit active in the wild. https://thehackernews.com/2025/07/urgent-google-releases-critical-chrome.html
- The Hacker News. (2025, July 15). North Korean Hackers Flood npm Registry with XORIndex Malware in Ongoing Attack Campaign. https://thehackernews.com/2025/07/north-korean-hackers-flood-npm-registry.html
- The Hacker News. (2025, July 16). Hackers Leverage Microsoft Teams to Spread Matanbuchus 3.0 Malware to Targeted Firms. https://thehackernews.com/2025/07/hackers-leverage-microsoft-teams-to.html
- Morphisec. (2025, July 16). Teams Call to Ransomware: Matanbuchus 3.0 MaaS Levels Up. https://blog.morphisec.com/teams-call-to-ransomware-matanbuchus-3.0-maas-levels-up
- BleepingComputer. (2025, July 13). Google Gemini flaw hijacks email summaries for phishing. https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/google-gemini-flaw-hijacks-email-summaries-for-phishing/
- 0din.ai. (2025, July 13). Phishing for Gemini. Mozilla GenAI Bug Bounty Program. https://0din.ai/blog/phishing-for-gemini
- The Hacker News. (2025, July 9). Iranian-Backed Pay2Key Ransomware Resurfaces with 80% Profit Share for Cybercriminals. https://thehackernews.com/2025/07/iranian-backed-pay2key-ransomware.html
- Morphisec. (2025, July 9). Pay2Key resurgence: Iranian cyber warfare. https://www.morphisec.com/blog/pay2key-resurgence-iranian-cyber-warfare/
- Unit 42. (2025, July 14). Behind the clouds: Attackers targeting governments in Southeast Asia implement novel covert C2 communication. https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/windows-backdoor-for-novel-c2-communication/
- The Hacker News. (2025, July 12). Weekly Recap: Scattered Spider Arrests, Car Exploits, macOS Malware, Fortinet RCE and More. https://thehackernews.com/2025/07/weekly-recap-scattered-spider-arrests.html
- Cyble. (2025, July 11). Hacktivists attacks on critical infrastructure surge in 2025. https://cyble.com/blog/hacktivists-attacks-on-critical-infrastructure/
- US Department of Justice. (2025, July 16). Armenian National Extradited to the United States Faces Federal Charges for Ransomware Extortion Conspiracy. https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/armenian-national-extradited-united-states-faces-federal-charges-ransomware-extortion
- Europol. (2025, July 17). Global operation targets NoName057(16) pro-Russian cybercrime network. https://www.europol.europa.eu/media-press/newsroom/news/global-operation-targets-noname05716-pro-russian-cybercrime-network
- Cloudflare. (2025, July 16). DDoS threat report for 2025 Q2. https://blog.cloudflare.com/ddos-threat-report-for-2025-q2/


